Determine Centers of Gravity
Centers of Gravity (CoG) can be determined using the following types of solve:
Number of CoGs
The Number of CoGs feature determines a specified number of centers of gravity (CoGs), representing possible locations for your distribution centers (DCs). These CoGs are calculated to minimize the overall travel distance to demand and/or supply locations.
You can configure this calculation by entering the desired number of CoGs (an integer between 1 and the total number of demand/supply locations you want to consider) into the Number of CoGs widget, then clicking the Solve Number of CoGs button.
Algorithm to determine CoGs using ‘Number of CoGs’
The algorithm identifies CoG locations based on the weighted “pull” of each demand and supply point (weighted by their respective load, demand or capacity). Each CoG is pulled toward the center of these weighted forces to minimize the overall travel distance.
For N CoGs, the algorithm:
Initializes with N starting CoG locations.
Assigns each demand/supply point to its nearest CoG.
Recalculates the CoG positions based on the assigned locations.
Repeats this assignment and update cycle until the system no longer continues to improve, at which point the algorithm is terminated with a stable state and minimal total travel distance.
Number of CoGs Initialization Strategies
The Number of CoGs final result may depend on the starting points in step 1 above. Different initial CoG placements can lead to different solutions in some cases. To improve accuracy, the algorithm can run multiple times from various starting positions and select the best result (the lowest total travel distance).
It is possible to choose the desired balance between speed and accuracy by:
Adjusting the setting Algorithm for # of CoGs on the CoG Settings page (dropdown).
Configuring the desired approach on the String Settings Sheet using the CoG Algorithm for Number of CoGs attribute.
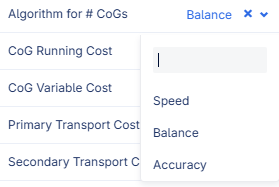
Available options for initialization:
Speed (Fastest) - Runs once using the largest demand locations as starting points. Fastest, but may miss better solutions.
Balance - Runs several times using a mix of high-demand, probabilistic, and random initializations. Balances speed and accuracy.
Accuracy (Slowest) - Runs many times with diverse initializations to avoid local optima. Most accurate, but slower.
This setting helps ensure that the CoG solution aligns with your priorities, whether that’s getting results quickly or achieving the most accurate solution.
Max Drive Time
In this type of solve, the Center of Gravity generates a grid of cities/locations on top of the data area and selects the minimum number of cities which can serve as DC, such that all customer locations can be reached within the specified maximum drive time. This means that for each demand/supply location, the drive time to its serving DC (center of gravity) will be at most the maximum drive time you specify. In the Maximum Drive Time widget you can specify the maximum number of hours that the demand/supply is allowed to travel from a DC to the demand location/the supply location. After entering this number, click on the Solve Max Drive Time button.
Constrained CoG
The Constrained CoG mode is an extension of the Max Drive Time CoG solve, which incorporates additional constraints and data from the SC Navigator input dataset. This model aims to minimize the number of CoG locations or to minimize overall costs, subject to various operational constraints. In this mode, if you include suppliers it will actually include the cost of sourcing and delivering the supply to the CoGs/DCs.
Data Inputs
Selected attributes from the following sheets can be included in this solve. If the data is not available, it will be considered as not restricted or not applicable.
Sheet |
Attribute |
|---|---|
Supplier Data |
‘Variable Cost’, ‘Fixed Cost’, ‘Minimum Capacity’, ‘Maximum Capacity’ |
Warehouse Data |
‘Minimum Capacity’, ‘Maximum Capacity’ |
Customer Product Data |
‘Variable Cost’, ‘Lead Time’, ‘Minimum Fulfillment Rate’ |
Note
The value Maximum Drive Time impacts the solution time. The smaller this value, the faster a solution will be found.
Constraints
The Constrained CoG mode offers the possibility to incorporates the following constraints, via the table “Constraint CoG”:
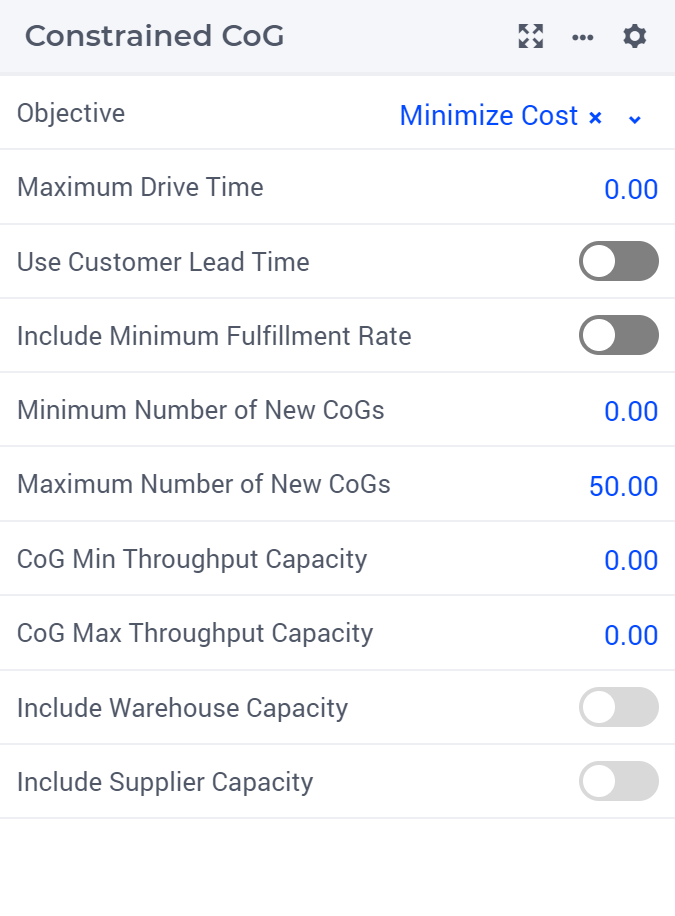
Maximum Drive Time - Customer
The drive time, between each CoG and all customer locations that are served by this CoG, should be within this value. This value is mandatory unless Use Customer Lead Time is used.
Maximum Drive Time - Supplier
The drive time, between each CoG and all supplier locations that serve this CoG, should be within this value. This value is optional: 0 means that supplier-CoG drive times are not restricted. This constraint applies only when suppliers are included in the solve.
Use Customer Lead Time
Each CoG should be located within the ‘Lead Time’ of the customer it serves. If a customer location has multiple Lead Time values for multiple customers/products/periods, the smallest value will be used.
Include Minimum Fulfillment Rate
The percentage of served demand of a customer location should be at least ‘Minimum Fulfillment Rate’. If a customer location has multiple Minimum Fulfillment Rate values for multiple customers/products/periods, the largest value will be used.
Minimum Number of New CoGs
The minimum number of CoGs to be generated. Default is 0.
Maximum Number of New CoGs
The maximum number of CoGs to be generated. Default is the number of customer locations.
CoG Min Throughput Capacity
The minimum capacity for all CoGs over the selected periods. If “Include Warehouse Capacity” is enabled and data exists for fixed locations, then that input data is used instead of this value. Zero means no minimum capacity.
CoG Max Throughput Capacity
The maximum capacity for all CoGs over the selected periods. If “Include Warehouse Capacity” is enabled and data exists for fixed locations, then that input data is used instead of this value. Zero means unlimited capacity.
Include Warehouse Capacity
For fixed warehouse locations, include warehouse minimum/maximum capacity. This value is calculated from ‘Minimum Capacity’ and ‘Maximum Capacity’ in Warehouse Data sheet. If there are multiple capacity values in multiple warehouses/periods, the total value of the included periods for each location will be used.
Include Supplier Capacity
For included suppliers, include supplier minimum/maximum capacity. This value is calculated from ‘Minimum Capacity’ and ‘Maximum Capacity’ in Supplier Data sheet. If there are multiple capacity values in multiple locations/periods, the total value of the included periods for each supplier will be used.
Note
Supplier (product) maximum capacity vs unlimited capacity:
If supplier maximum capacity is zero and some product level maximum capacity is zero: capacity is treated as unlimited.
If supplier maximum capacity is zero and all product level maximum capacities are non-zero: the sum of all product level maximum capacities is used.
If supplier maximum capacity is non-zero: supplier maximum capacity is used.
Note
Supplier-only Constrained CoG requirements and behavior:
Selected suppliers must specify a minimum and/or maximum capacity.
Supplier flow volume = maximum capacity where available; otherwise minimum capacity.
If neither is provided, the solve stops with an error message.
Option ‘Include Supplier Capacity’ is automatically enabled.
Objectives
There are two objectives to choose from, the choice can be made in the above mentioned “Constrained CoG” table:
Minimize Number of CoGs The solution will generate the minimum number of CoGs that meet all included constraints.
Minimize Total Cost There are four categories of cost and their calculation detail is described in the table below.
Category |
Detail |
|---|---|
Supplier Cost |
|
Warehouse Cost |
|
Customer Cost |
|
Transport Cost |
|